Health
Signs of Gout: Is Pain and Swelling in the Big Toe the Cause?
Gout is a noteworthy health issue, and the appearance of swelling and pain in the big toe often makes many people wonder if it is a sign of this disease. This article will take you on a journey to explore the characteristic manifestations of Gout and whether their appearance means having Gout. Let’s find out together to better understand this medical condition and how to recognize the important signs.
I. Gout and why swelling and pain in the big toe are often considered characteristic symptoms of this disease
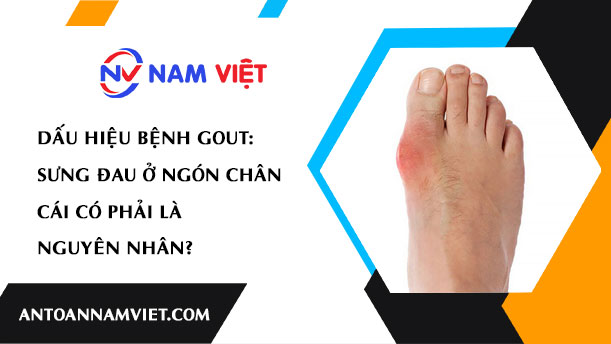
Gout, a common form of inflammatory arthritis, often manifests through pain and swelling in the joints, especially in the big toe. This is not just a random manifestation, but a characteristic sign of the disease, closely related to the mechanism of Gout’s formation and development.
Nature of Pain and Affected Area: The pain in Gout usually appears intensely and greatly affects the patient’s mobility. For many people, pain often arises at night or after eating foods rich in purines such as red meat, seafood. The affected area is usually the big toe, ankle joint, knee, wrist, and elbow.
Swelling and Physical Appearance: The affected joint becomes swollen, painful, hot, red, and feels tender to the touch. This characteristic is due to the inflammation and the formation of urate crystals accumulating in the joint. It not only causes the affected area to lose flexibility but also creates the characteristic physical appearance of Gout.
Pain Cycle and Gradual Reduction: Gout pain usually reaches its peak within the first 4-12 hours after it appears and gradually subsides within about two weeks. Although the patient may no longer feel pain after this time, Gout has not completely disappeared and can recur if not strictly controlled and lifestyle changes are not made.

II. Signs and symptoms of Gout, including pain, swelling, and commonly affected joint areas
Gout presents with characteristic signs and symptoms, creating a clear picture of its effect on the body. These signs include pain, swelling, and specific impacts on important joint areas.
Uncomfortable Pain and Specific Intensity: One of the clearest signs of Gout is a specific and uncomfortable pain. The pain often appears suddenly and can reach an extremely high level, greatly affecting mobility and daily life. Over time, the pain can become more severe if not controlled.
Swelling and Sensation of Heat and Redness: Another clear manifestation of Gout is swelling in the affected joint area. Not only does it cause a loss of flexibility, but the swelling is also accompanied by a feeling of heat and redness at the joint location. This is the result of inflammation and the accumulation of urate crystals, creating a characteristic physical appearance of the disease.
Diverse Effects on Joints: Gout does not just focus on one specific area but also affects many different joint areas. The big toe, ankle joint, knee, wrist, and elbow are often locations frequently affected by the disease. This creates a comprehensive picture of the widespread impact of Gout on the joint system.

III. The severity of Gout pain, its duration, and how it gradually subsides after the first 4-12 hours
The pain in Gout is not only distinctive in its level of discomfort but also affects the mobility and quality of life of the patient. Speaking of the severity of Gout pain and how it changes over time, we can better understand the nature of this disease.
Prominent Characteristics of the Pain: Gout pain often starts suddenly, and its intensity can be particularly high. This reduces mobility and creates a state of severe discomfort. Often, the pain appears at night or after eating a lot of purine-rich foods, increasing the risk of a pain attack.
Duration and Discomfort: Gout pain typically lasts for about 4-12 hours from its onset, creating an extended cycle of intense pain. During this time, patients often face discomfort and insomnia due to the pain. However, a characteristic feature of Gout is that the pain naturally subsides after this period.
Gradual Subsidence and Milder Sensation: Although it starts intensely, Gout pain usually subsides within the first two weeks. This provides an opportunity for the patient to recover and resume daily activities. This gradual reduction often happens naturally but can be more stable when combined with treatment measures and lifestyle control.

IV. The cause of gout, related to uric acid and how the body cannot process it, leading to the formation of urate crystals
Gout originates from a sudden increase in uric acid in the body, leading to the process of urate crystal formation. This is closely related to how the body processes uric acid and the crystal formation process, providing an important basis for understanding the cause of this disease.
The Increase of Uric Acid: Uric acid, a substance remaining from the digestion of purines, can increase suddenly in the body. This can happen because the kidneys cannot eliminate uric acid fast enough, or the body produces too much uric acid from food and the body’s basic quality.
The Body’s Limited Processing Ability: Gout patients often have a limited ability to process uric acid. This may be because the kidneys do not eliminate uric acid efficiently enough, or because the body produces excessive uric acid. This leads to the accumulation of uric acid in the body, creating favorable conditions for the formation of urate crystals.
The Formation Process of Urate Crystals: When uric acid accumulates at high levels, it can combine with mineral salts in the blood to form urate crystals. These crystals can concentrate in the joints and surrounding tissues, causing irritation and triggering inflammation and pain, highlighting the characteristic symptoms of Gout.
Link to Symptoms of Pain and Swelling: When urate crystals accumulate in the joint areas, they create a strong irritation for the body, causing pain and swelling. These crystals can also create an inflammatory condition around the joint, painting the characteristic and painful symptom picture of Gout.

V. Methods for treating and controlling Gout
Gout, although there is no definitive cure, has many means and strategies to control symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Lifestyle and Nutritional Changes
- Diet Adjustment: Avoid purine-rich foods such as shrimp, crab, and animal organs. Limit meat portions and replace with eggs, vegetables, and fruits. Drink enough water to enhance uric acid excretion through urine.
- Physical Activity: Engage in activities like walking, cycling, swimming to control weight and reduce uric acid levels in the blood. Exercise also helps reduce inflammation and restore joint flexibility.
- Weight Control: Maintain a stable weight to reduce pressure on joints and decrease the risk of increasing uric acid levels.
Medications
- Anti-inflammatory and Pain-Relief Drugs: Use drugs like NSAIDs to reduce pain and inflammation during an acute Gout attack.
- Uric Acid Production Inhibitors: Allopurinol and Febuxostat help reduce uric acid production, lowering the risk of recurrence.
- Uric Acid Excretion Drugs: Probenecid enhances the elimination of uric acid through urine.
- Anti-Urate Crystal Drugs: Colchicine helps prevent the formation and storage of urate crystals.
Prophylactic Treatment (Prophylaxis)
- Control Uric Acid Levels: Monitor uric acid levels in the blood and maintain them at a stable level to prevent new Gout attacks.
- Lifestyle Changes: Rest and Stress Reduction: Stress reduction measures and ensuring sufficient healthy sleep help control factors that trigger Gout pain.
Surgery
In severe cases, when traditional treatment measures are not effective, surgery may be performed. Synovectomy (removing part of the joint lining) or joint replacement are methods that a doctor might consider.

VI. Medications used to treat acute gout attacks and prevent future flare-ups
In the process of treating Gout, using medications is a crucial part to relieve pain during acute attacks and prevent future recurrences.
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs)
- Function: Reduce pain and inflammation.
- Examples: Ibuprofen, Naproxen.
- How to Use: Take according to the doctor’s prescribed dosage during an acute Gout attack.
2. Colchicine
- Function: Prevents the formation and storage of urate crystals.
- How to Use: Used during an acute Gout attack. A high initial dose, then reduced to prevent recurrence.
3. Glucocorticoids (Corticosteroids)
- Function: Reduce inflammation and pain.
- Example: Prednisone.
- How to Use: Taken orally or injected into the affected area depending on the severity of the pain.
4. Uric Acid Production Inhibitors
- Function: Reduce uric acid production, lowering the risk of recurrence.
- Examples: Allopurinol, Febuxostat.
- How to Use: Taken as prescribed by the doctor, usually long-term to control uric acid.
5. Uric Acid Excretion Drugs
- Function: Enhances the elimination of uric acid through urine.
- Example: Probenecid.
- How to Use: Taken at the recommended dosage, often used in cases where uric acid production inhibitors cannot be used.
6. Colchicine Prophylaxis
- Function: Prevents acute Gout attacks.
- How to Use: Used in a low daily dose to prevent pain recurrence.
7. NSAIDs Prophylaxis
- Function: Prevents acute Gout attacks.
- How to Use: Used as prescribed by the doctor to prevent new attacks.
The process of treating and preventing Gout often requires a flexible combination of the above medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional. This helps achieve optimal effectiveness in controlling symptoms and the risk of disease recurrence.

VII. Surgical methods in severe cases and potential complications if Gout is not well controlled
In severe cases of Gout, when traditional treatment measures do not achieve the desired effectiveness, surgical methods may become the final option.
Synovectomy (Surgical Removal of Joint Lining)
- Function: Removes excess synovial fluid accumulated in the joint, reducing swelling and pain.
- Procedure: The doctor performs this by aspirating synovial fluid or through arthroscopic surgery.
2. Joint Replacement
- Function: Replaces the damaged joint with an artificial joint.
- Procedure: For cases where Gout causes severe damage, joint replacement may be necessary to restore function and reduce pain.
3. Tophus Removal Surgery (Removal of Urate Crystals)
- Function: Removes urate crystals (tophi) accumulated in the joint.
- Procedure: The doctor performs this via open or arthroscopic surgery to remove the urate crystals, reducing pressure and inflammation.
Complications If Gout Is Not Controlled
If Gout is not well controlled, it can lead to serious health complications:
Joint Destruction (Arthropathy)
- Description: Accumulated urate crystals can cause severe damage to the joint, leading to joint destruction and reduced function.
2. Kidney Stones
- Description: If uric acid is not properly eliminated, it can form kidney stones, posing a risk of serious kidney problems.
3. Heart and Vascular Disease
- Description: Gout can be associated with cardiovascular problems such as high blood pressure, stroke, and heart disease.
4. Erectile Dysfunction
- Description: Gout may also increase the risk of erectile dysfunction in men.
5. Endocrine Complications
- Description: A sudden increase in uric acid can cause endocrine problems, especially when the disease is not controlled.

An Toan Nam Viet – a leading unit in providing occupational safety training and workplace environmental monitoring services. We are proud to be a trusted partner for businesses, helping ensure a safe working environment and protecting workers' health.With extensive experience and a team of top experts, we are committed to delivering high-quality services while meeting all regulatory requirements on occupational safety and environmental monitoring.
Our occupational safety training services include educating and raising awareness among employees about safety regulations, equipping them with skills to handle dangerous situations, and implementing accident prevention measures. We continuously update and apply the latest knowledge to ensure your employees always work in a safe environment, minimizing the risk of occupational accidents and protecting their lives.
With our workplace environmental monitoring services, we use the most advanced equipment and methods to measure, monitor, and analyze the quality of air, water, and noise in the working environment. We provide detailed and accurate reports on pollution levels, helping businesses implement solutions to improve working conditions, ensure legal compliance, and create a healthy workplace for employees.
Contact Information:
- Nam Viet Occupational Safety Training and Environmental Monitoring Co., Ltd.
- Phone: 0908 111 791
- Email: lienhe@en.antoannamviet.com
- Website: https://en.antoannamviet.com