Safety Document Group 3
Occupational Safety Training Document for Air Traffic Control
DOWNLOAD LABOR SAFETY DOCUMENT SET (6 GROUPS, OVER 300 INDUSTRIES)
The materials of the labor safety training course in air traffic control operations help workers equip safety knowledge and prevent hazards while working in aviation.
Chapter 1: Current Situation of Air Traffic Control Industry, Remote Control Operations via Computers
1. Aviation safety situation worldwide and in Vietnam
The worst accident in 2019 was the Ethiopian Airlines Boeing 737 MAX crash on March 10, 2019, killing 157 people. The number of deaths in global aviation accidents decreased by more than half in 2019, according to the latest report from an aviation consulting company.
Bloomberg, citing To70 data, showed that 257 people died in 8 fatal aviation accidents in 2019. This represents a significant decrease compared to 534 deaths in 13 aviation accidents in 2018.
The number of fatalities spiked in December 2019 after the Bek Air Fokker 100 crash in Kazakhstan, killing 12 people.
The worst accident in 2019 was the Ethiopian Airlines Boeing 737 MAX crash on March 10, 2019, killing 157 people.
Air traffic controllers are likened to guardians of the sky, ensuring air traffic is safe, orderly, and fast. The history of aviation has recorded many accidents caused by this sector.
176 deaths due to controllers speaking their native language
- In the mid-1970s, the Zagreb Air Traffic Control Center in Yugoslavia (now Croatia) managed the busiest airspace in Europe, as Zagreb was a hub for flights from Northern Europe to Southeast Europe, the Middle East, and Asia.
- On September 10, 1976, British Airways Flight 476, a Hawker Siddeley Trident flying from London to Istanbul, collided with Inex-Adria Avioproment Flight 550 from Split, Yugoslavia, to Cologne, West Germany, in the airspace near Zagreb.

- The collision was attributed to the Zagreb air traffic control center. That day, the center was understaffed, and the team was overworked. Adria 550 requested a change in altitude to fly higher. The controller approved without realizing that the British Airways plane was at the same altitude. When the accident was imminent, the controller hurriedly warned Adria 550 not to ascend further, but he panicked and spoke in his native language instead of English.
- All 176 people on both flights died. To this day, this remains the only fatal accident involving a British Airways aircraft and is the deadliest aviation accident in Croatia.

Mid-air collision over Uberlingen, Germany
- A terrible aviation accident occurred in southern Germany on July 1, 2002, when two planes collided mid-air, killing most of the 71 passengers on both aircraft, mostly children.
- The planes involved were DHL Flight 611 from Milan to Brussels and Bashkirian Airlines Flight 2937 from Moscow to Barcelona, Spain. The cause was attributed to air traffic controller error. That day, a Skyguide controller managed two sectors simultaneously and allowed the Russian plane to descend.
- Meanwhile, the DHL plane followed TCAS instructions (Traffic Collision Avoidance System, independent of ATC) instead of ATC guidance, descending to avoid a collision, which led to the accident.
Controller fell asleep, 178 deaths in Russia
- At 5 a.m. on October 11, 1984, Aeroflot Flight 3352 from Krasnodar to Novosibirsk, preparing to land at Omsk airport, encountered a runway maintenance operation requested to dry the runway after rain, but the air traffic controller forgot to alert other departments that the runway was not ready and fell asleep.
- At 5:25 a.m., the maintenance team placed 3 vehicles with 7 tons of fuel on the runway. The plane could not see them from the air. When approaching landing, they tried to contact the controller but failed. The plane landed, and the accident caused the death of 178 people.
- Similarly, in Hai Phong’s Cat Bi airport on March 9, 2017, a controller fell asleep while operating flights, causing two aircraft to lose contact for 30 minutes, delaying landing procedures and forcing planes to circle in the sky.
2. Characteristics of Air Traffic Control, Remote Operations via Computers
Air Traffic Control (ATC) guides aircraft during takeoff and landing, two crucial stages of a flight. Departure times depend on controller instructions before pilots can taxi to the runway.
Aviation operates 24/7, so ATC operates continuously. Unlike other professions, controllers work two 12-hour shifts per day.
During flight operations, ATC guides takeoff and landing. For takeoff, pilots receive detailed instructions including taxiway positions, runway coordinates, and weather conditions, which they read back for confirmation.
At departure, pilots follow ATC instructions to taxi and take off. Once airborne, the plane is handed to approach control and then to en-route control once reaching cruise altitude (~3,000 m). Near the destination, pilots contact ATC for descent and landing guidance.
According to a U.S. study, over 60% of air traffic controllers admit to falling asleep or having health issues during continuous duty. Heavy workloads often lead to fatigue, reduced alertness, and risk to national aviation safety.
Chapter 2: Factors Affecting Operation and Control
1. Work posture in air traffic control safety materials
Poor posture can restrict blood flow, affecting circulation, reducing work efficiency, and lowering immunity.
a. Neck tilted backward
Sitting too low relative to the computer may force the neck backward, increasing the risk of cervical spine degeneration.
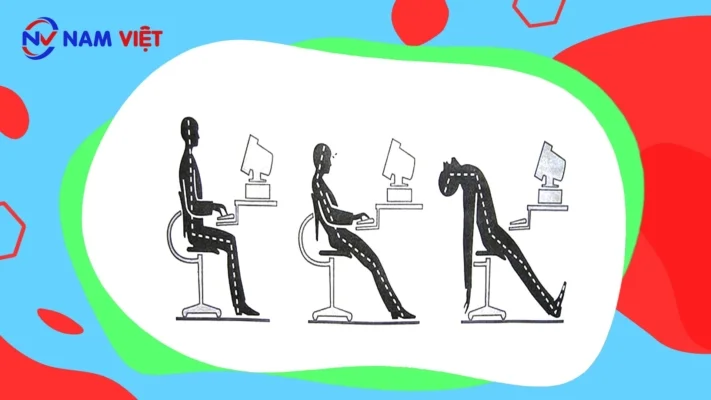
b. Head resting on desk
Habitually resting the head on the desk can cause neck, shoulder, and cervical spine pain, leading to long-term spinal degeneration.
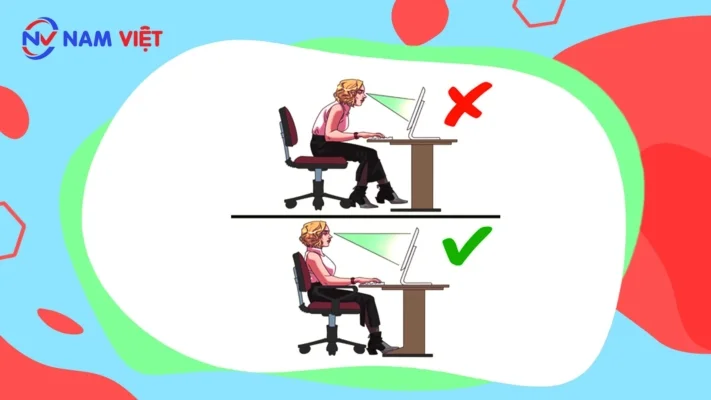
c. Incorrect distance from eyes to screen
Eyes should align with a point 5–7 cm below the top edge of the screen, approximately 50 cm away. This keeps the head straight and relaxed.
d. Back not straight
Experts advise keeping the back straight along the chair to reduce fatigue.
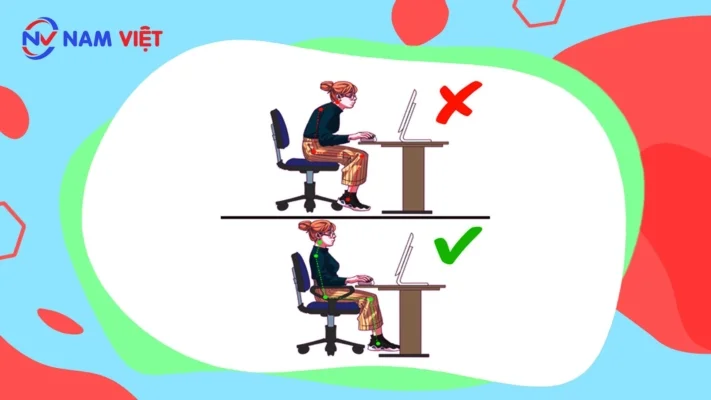
e. Feet not touching the floor
Adjust chair height so feet rest flat, thighs and calves form slightly over 90°, back straight, ideally remove shoes for comfort.
f. Crossing legs
Crossing legs restricts blood flow and may increase blood pressure; standing or stretching is recommended.
g. Not using supportive equipment
Use backrests, seat cushions, or footrests to maintain proper posture for comfort and productivity.
h. Not adjusting posture
Even minor adjustments are important for comfort; standard chairs may not provide needed support.
i. Not adjusting chair height
Adjust height so hips are slightly higher than knees.
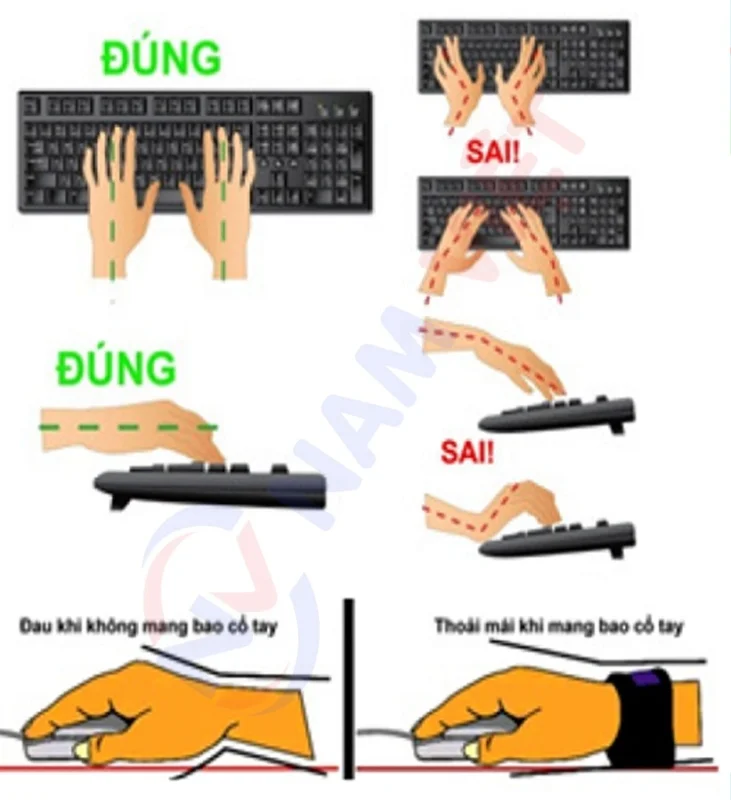
k. Incorrect arm posture
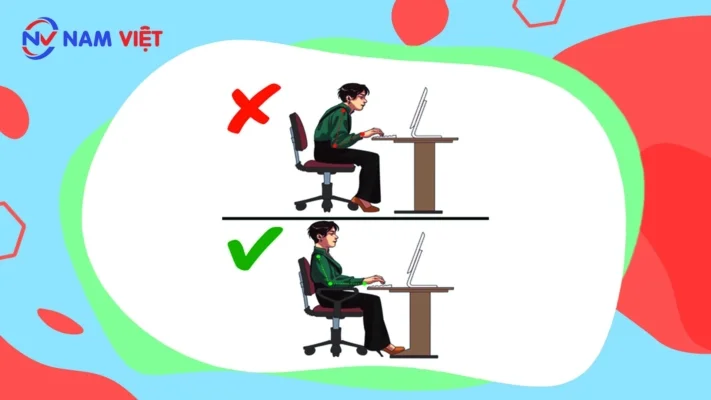
The correct posture is to keep your arms bent at a right angle of 90° when typing or working on a computer. You should avoid resting your wrists on the keyboard while typing and use your whole hand to hold and move the mouse comfortably.
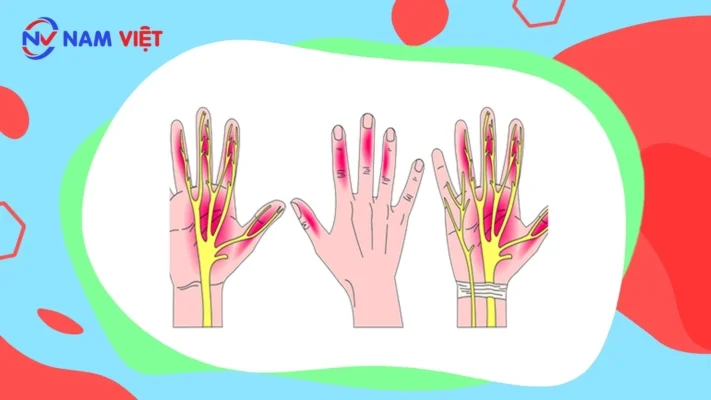
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when you perform activities that involve frequent wrist flexion and extension or repetitive lifting of the arms, such as typing on a computer, holding a phone, or gripping a car steering wheel.
Symptoms develop gradually, often worse in dominant hand. Thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers may feel numb or tingly, especially at night.
2. Working hours
Air traffic controllers often have to work under high pressure, especially when they are the only person in the control room and are never able to take adequate breaks.
Air traffic control is a job directly related to flight safety. However, the challenges and effort behind the work are little known.
Controllers must continuously speak and provide instructions to pilots (during peak periods, the speaking and flight guidance time of an air traffic controller can exceed 50 minutes per hour). At the same time, they must monitor screens with their eyes, listen to pilot reports through headsets, write with one hand (using a two-color pen) or operate the computer keyboard to manage electronic functions, while the other hand controls communication systems such as “ground-to-air” and “ground-to-ground.” Sometimes, they also use their feet to press buttons for receiving or disconnecting communications under the desk.

Shift duration is 2 hours maximum. During this time, focus must be full; no personal calls, no leaving posts, no distractions. Breaks allow coffee, review, or rest.
Ron Connolly, former Charleston International Airport controller with 10 years experience, told CNN he often slept 4 hours or less per day.
“I worked exhausted, never fully rested between shifts, and starting and ending on the same day was rare,” said Connolly.

He added: “I was extremely tired and in pain, especially during overnight shifts as the only person in the control room.”
Reports indicate this is not unique; a controller at Ronald Reagan Airport, Washington, D.C. also fell asleep due to fatigue.
3. Common health risks
Eye strain from prolonged screen time can lead to eye irritation, dryness, fatigue, and reduced vision. According to a recent report, these issues are on the rise.
Dr. Christopher Starr, Associate Professor of Ophthalmology at Weill Cornell Medical College, stated: “Some individuals use electronic devices for up to nine hours a day. The eye muscles must focus at close distances, which causes fatigue.”
Scientific studies show that excessive time spent in front of electronic screens affects both behavior and brain structure. Specifically, excessive smartphone use has been linked to anxiety, stress, and even depression.
Researchers refer to this as “digital dementia,” noting that excessive screen time negatively impacts brain functions such as short-term memory, focus, and attention.
Prolonged computer use also increases exposure to electromagnetic radiation and heat, which can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath, headaches, and insomnia. In some cases, increased exposure has been associated with various types of cancer. Skin damage may also occur.
Recent studies additionally indicate that radiation from laptops can negatively affect cells, damage DNA, and impair reproductive ability.
a. Prolonged sitting in front of computers affects eyesight in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- Due to the nature of air traffic controller work, they often sit at computers for hours without realizing that their eyes rarely blink while looking at the screen. Prolonged exposure can lead to eye fatigue, gradual vision deterioration, blurred vision, and eventually myopia.
b. Prolonged sitting in front of computers accelerates skin aging in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- In practice, individuals who frequently use computers and electronic devices show signs of faster skin aging compared to others, even when consuming fresh and healthy foods. The cause is that electromagnetic waves can affect lymphatic drainage, impairing the removal of waste from body tissues and cells, negatively impacting collagen structures under the skin. Over time, skin becomes more vulnerable, weaker, pale, prone to acne, and harder to recover. Hours of sitting in front of a computer can lead to early signs of aging. Every facial movement in front of a computer screen affects your face. This includes actions such as frowning, squinting, or bending your neck for long periods. Consequently, we may develop early aging symptoms such as wrinkles on the face, forehead, eyes, and neck. A detailed breakdown includes:
- Squinting or frowning while reading on the computer (to focus) can cause forehead wrinkles.
- Bending your neck for too long can shorten your neck muscles.
- Sitting in one posture for extended periods can also contribute to a double chin.
- All these factors demonstrate the effects of laptop radiation and their harmful impact on skin and user health.
c. Allergies leading to skin aging in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- People with skin issues, such as sun sensitivity or rosacea, are at higher risk. Screens tend to generate an electrostatic field, attracting airborne dust that settles on the skin, causing irritation, dryness, and allergic reactions.
- Olle Johansson, Associate Professor at the Department of Experimental Dermatology, Karolinska Institute, describes overexposure in sensitive individuals as “screen dermatitis.” This condition occurs when skin cells are affected by continuous exposure to electromagnetic fields and light.
d. Prolonged computer use causes shoulder and back pain in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- Normally, after sitting for more than three minutes, people begin to slouch or cannot maintain an upright posture. Extended sitting causes wear on joints and significant strain on spinal ligaments due to prolonged weight on shoulders and back. Additionally, when focusing on a computer, you instinctively lean your neck forward, causing tension in the neck and shoulders. A Penn State study indicated that sitting in front of a computer for at least four hours increases pressure on lumbar discs, which can lead to herniated discs—a “work-related disease” associated with back pain from prolonged computer use. Therefore, standing and moving is important. Research shows that changing positions every 15 minutes prevents adverse effects on spinal discs. Contrary to common belief, rest alone is not as effective as movement, which significantly alleviates back pain. According to the Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development, just 25 minutes of aerobic exercise, such as running or swimming, can reduce back pain by 28%.
e. Prolonged and frequent computer use can impair cognition in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- A study involving 1,600 adults and 65 elderly individuals found that people with genes associated with dementia had nearly double the risk of developing the disease compared to those without the genes. However, among those who did not exercise regularly, the risk was similar. This is directly relevant to people sitting long hours at computers. American psychologist Michael Pietrus states: “Excessive computer stimuli cause distraction and reduce work efficiency.” Frequent exposure to such stimuli can lead to forgetfulness and mental lapses.
- To avoid these issues, clearly define work goals, such as completing weekly reports, and set rules to limit access to social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter. Instead of sitting passively and staring at screens, take breaks to move every 1–2 hours to relax joints and improve circulation.
f. Prolonged sitting affects the respiratory system in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- Prolonged computer use is a low-energy activity. Sitting restricts lung expansion, limiting oxygen intake, which often leads to shallow breathing. Over time, this reduces the lungs’ oxygen absorption capacity, affecting blood oxygen levels and overall organ function. According to research from the California Science Institute (USA), sitting more than five hours per day reduces mental alertness, immunity, and heart function by at least 10%. To counteract this, occasionally take deep breaths. Practicing yoga can help regulate breathing efficiently. Regular physical activity and a balanced diet and rest are also recommended.
g. Prolonged sitting affects the cardiovascular system in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- Sitting affects lung function, which in turn impacts the cardiovascular system. The heart and cardiovascular system function better through standing and moving. A 2010 study found a 125% increase in cardiovascular disease risk due to prolonged sitting, along with a 46% increased risk of mortality from other causes.
h. Prolonged sitting may increase blood sugar in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- A 2013 Chester University study found sitting burns 21% fewer calories per minute than standing. Recent research from a Florida university showed that prolonged sitting can raise blood sugar levels, even in individuals with healthy weight. Sedentary adults may have Hemoglobin A1C levels of 5.7% or higher, considered prediabetic by the American Diabetes Association. Despite healthy weight, they may have higher fat percentages (around 25% or more), leading to metabolic issues such as high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, and high cholesterol. The CDC notes that a 5–7% weight loss and 150 minutes of weekly exercise can delay or prevent diabetes onset.
i. Prolonged sitting may cause infertility in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- Extended inactivity reduces blood supply to organs and oxygenation, and electromagnetic radiation can hinder circulation, leading to blocked blood flow, particularly in the pelvic region and lower limbs. This habit can contribute to infertility.
j. Prolonged sitting may cause hemorrhoids in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- Currently, over 50% of the Vietnamese population suffers from hemorrhoids, particularly office workers, pregnant women, and heavy laborers. Prolonged sitting increases the risk; studies show that frequent prolonged sitting raises hemorrhoid risk to 72.9%, while active individuals have a 43% risk. Balancing work and rest is crucial for prevention and recovery.
k. Increased risk of cancer in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- Prolonged sitting may increase colon, breast, and uterine cancer risk. The mechanism is not fully understood but may relate to excess insulin production promoting cell growth. Physical activity increases antioxidants, helping eliminate cancer-causing free radicals. A meta-analysis of 43 German studies with over 4 million participants found sedentary individuals had a 24% higher risk of colon cancer, 32% higher risk of endometrial cancer, and 21% higher risk of lung cancer. Weight gain, hormonal changes, metabolic dysfunction, and inflammation also contribute to cancer risk.
- Prolonged sitting can also increase mortality risk. A study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, covering 54 countries, analyzed sitting more than three hours daily. Results showed over 60% of people worldwide sit for more than three hours daily, contributing to approximately 433,000 deaths annually from 2002 to 2011. The global average sitting time is 4.7 hours/day. Reducing sitting time by 50% can lower mortality risk by 2.3% from all causes.
l. Infections in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- Recent studies indicate that most keyboards and mobile phones harbor numerous bacteria and microorganisms. Besides spreading common illnesses like colds and flu, contaminated devices can transmit staphylococcus and other serious infectious diseases.
Chapter 3: Remedies
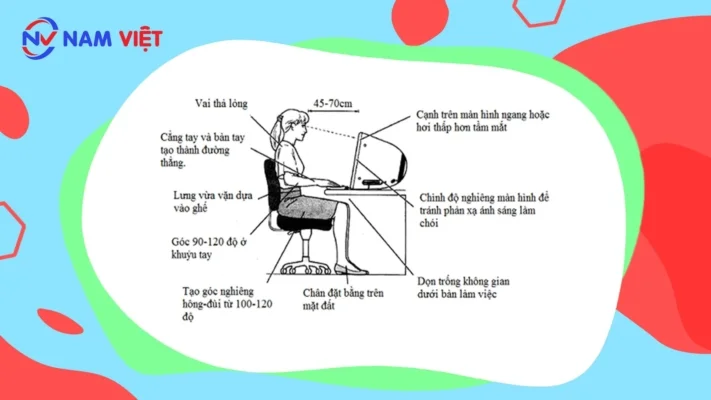
1. Maintain proper posture while using a computer in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
Depending on your body type, adjust chair height to achieve a “standard” posture to avoid eye and spinal problems.
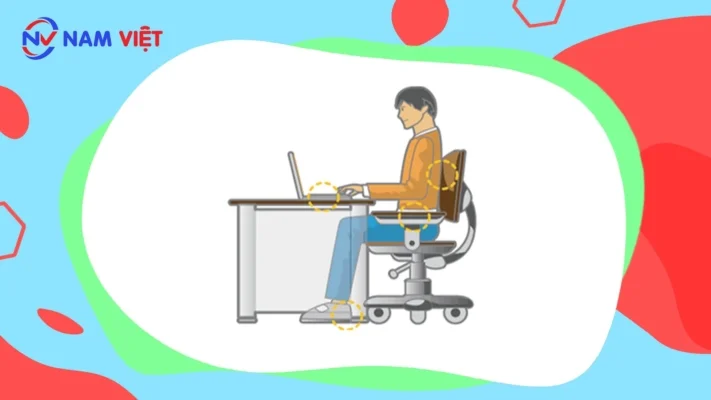

Correct sitting posture while working on a computer:
Hand posture: Always keep your arms at a 90-degree angle at the elbows while typing or performing other tasks with the keyboard or mouse.
Avoid resting your hands heavily on the keyboard or mouse and do not apply excessive force when typing or clicking.
Reducing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
To reduce the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome, especially for office workers frequently using computers, apply the following measures:
- Keep hands on the same plane as the forearms.
- Do not grip tools too tightly.
- Do not type too forcefully.
- Switch hands when possible.
- Rest and relax every 15–20 minutes.
- Keep hands warm in cold environments.
- Do not rest your head on your hands while sleeping.
- Avoid stress.
For office workers, simple exercises at the desk or whenever possible can help prevent discomfort caused by carpal tunnel syndrome.
2. Eye breaks in Air Traffic Control Safety Documents
- Prolonged screen focus causes eye strain and reduced vision. Therefore, regular eye breaks are necessary. Every 30–45 minutes, perform eye relaxation exercises such as:
- Look straight, then right, left, up, and down for 10 seconds each.
- Close eyes and gently rub the eyeballs with your hands for 10 seconds.
- Squint and then open eyes rapidly for 10 seconds.
Note: Adjust screen brightness for comfort; avoid excessive brightness.
- Follow the 20-20-20 rule: For optimal eye health, every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet (6 meters) away for 20 seconds.

-
- Mayo Clinic doctors introduced the 20-20-20 rule to rest eyes while focusing on screens. Closing eyes or blinking periodically helps moisten the eyes, which tend to dry during screen use.
- Additional eye relaxation methods for prolonged computer use include:
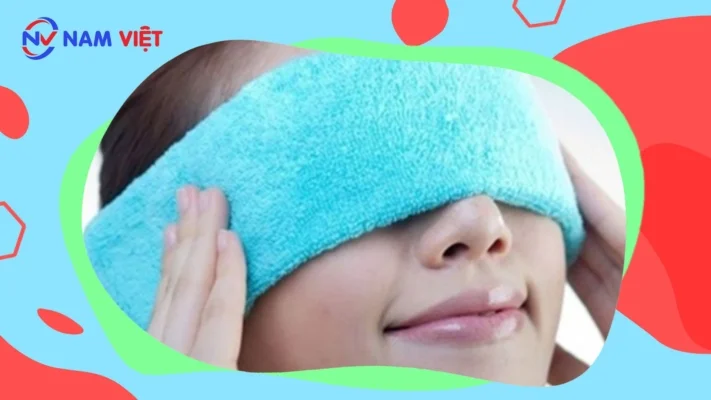
- Warm compress: Extended computer or phone use can cause headaches, shoulder pain, eye strain, and dry eyes, especially at a distance.
- Apply a warm cloth to the eyes to relax, reduce pain, and relieve discomfort such as:
- Dry eyes: Moisturizes and relieves dryness discomfort.
- Conjunctivitis: Reduces pain from eye infections.
- Styes or chalazion: Heat loosens blocked oil glands, reducing swelling.
- Blepharitis: Keeps eyelid oil glands clear, reducing inflammation.
- Eye twitching: Heat relaxes muscles, relieving symptoms.
- Warm compress procedure:
- Step 1: Fill a bowl with warm water, not too hot.
- Step 2: Soak a clean cloth completely.
- Step 3: Wring out excess water, keeping some moisture.
- Step 4: Fold the cloth into a rectangle and place over eyes.
- Step 5: Keep still for a few minutes to relax eyes.

-
- Reheat the cloth as needed. Repeat multiple times a day, using a clean cloth each time.
- Additional precautions:
- Eyes are sensitive. Avoid harmful actions:
- Use only clean water and cloth.
- Avoid gel or chemical eye packs; they may burn eyes or surrounding skin.
- Ensure water is warm, not hot.
- Use separate cloths for infected eyes to prevent cross-contamination.
- Eyes are sensitive. Avoid harmful actions:

- Other eye relaxation methods
- Wearing protective glasses
- In addition to sunglasses and protective glasses for sports, shooting, drilling, cutting, or other occupational activities, there are now glasses that help block blue light emitted from computer screens, phones, and TVs, helping to protect your eyes and worth considering.
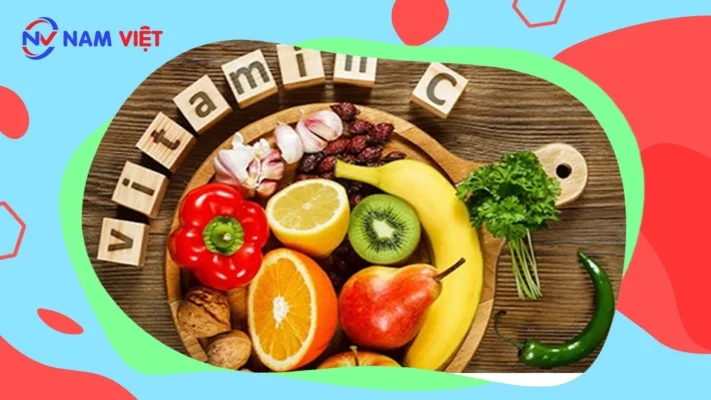
- Providing sufficient vitamins and nutrients
- Nutrients such as omega fatty acids and leafy greens, as well as vitamins A, C, and E, are essential for maintaining healthy vision, while lutein and zeaxanthin can help protect the macula and retina.
- Wearing protective glasses

-
-
- Provide sufficient vitamins to keep your eyes healthy
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle
- Monitor weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, and especially quit smoking. Smoking is a major risk factor for macular degeneration. In addition, people with diabetes should schedule regular eye check-ups and closely monitor blood sugar levels.
- “Focus” your eyes on something other than the screen
- Vision exercise: Place a pencil 15–20 cm from your eyes and focus on it for 10–15 seconds. Then shift your gaze to an object about 3 m away for 10–20 seconds, then back to the pencil. Repeat this cycle three times. First look straight, then glance left and right. Hold each side for 5 seconds, repeating three times alternately. Move your eyes up and down five times, holding each position for about 3 seconds. Do the same for diagonal eye movements, in a triangle or circular pattern. Blink continuously 10–15 times; ideally do this for 2 minutes. Let your eyes rest in darkness by covering them with your hands for 5 minutes.
-
- Optimize the workspace for frequent computer users:
- Besides screen time, the monitor position and lighting conditions are factors causing digital eye strain.
- Optimally, the center of your screen should be about 5 inches (12 cm) below eye level. This makes you look slightly downward at the screen instead of straight on, reducing eye strain; keeping your eyes at least 20 inches (50 cm) from the screen also achieves a similar effect.
- Since glare from the screen is inevitable, control glare from other light sources. Try using lower wattage bulbs or filter sunlight through curtains or blinds.
- Finally, frequent computer users may need to visit an eye clinic to treat computer vision syndrome. Doctors can prescribe specially designed lenses to minimize the effects of digital glare and improve vision and comfort.
- Doctors may also prescribe corrective lenses to address computer vision syndrome issues; these can be designed with technologies that reduce its effects. If these treatments are insufficient, doctors may recommend eye exercises at home or at the office.
3. Perform simple exercises in the air traffic control safety document

- Use break reminder software
- If you cannot manage your exercise or eye/body breaks proactively, you can use break reminder software.
- This software allows you to set specific time intervals (30, 45, 60, 90 minutes), at which point a notification appears on the screen. That is the moment to do some exercises, take a break for your eyes, or do other relaxation activities.
- Change sitting posture
- Most of us sit incorrectly. Spinal and muscular issues arise from bad habits. Proper posture: sit upright. If your chair is adjustable, make the backrest perpendicular to the seat. Relax shoulders, extend them backward. Keep the screen at eye level. You can use a laptop stand or desk riser if your desk is too low. Do not rest your wrists on the keyboard or mouse pad, as it may cause carpal tunnel syndrome. Keep both feet flat, knees slightly higher than hips. Use a footrest if necessary.
- Cervical spine misalignment
- This is common among office workers spending long hours in front of computers. Keeping your neck still for long periods reduces blood circulation, leading to joint degeneration and cervical misalignment, eventually affecting the back, hips, and shoulders.
- Prevention: keep your neck warm. Adjust office temperature to 26–28℃. Take a few minutes to move, e.g., rotate your torso, turn your neck left and right, bend forward, tilt backward.
- Stretch muscles every 20–45 minutes
- Many basic stretching exercises can improve your bones and muscles. Stand straight, interlace your hands, stretch upward. Stretch side muscles by tilting left and right. Bend forward with straight legs, touching your toes. Rotate or bend your neck in four directions (forward, backward, left, right) to improve flexibility and reduce shoulder and neck pain.
- Stand up and … use the restroom
- Simply standing and moving helps muscles stay flexible. Stretching exercises target specific areas, but movement activates the entire body. Eyes get a break and exposure to natural light instead of LED screen light. During movement, you can also do shoulder rolls, wrist rotations, or hip twists.
- Depression and schizophrenia
- Excessive computer work, overwhelming tasks, and lack of mutual support among employees contribute to increasing rates of depression in office workers.
- Prolonged depression may lead to schizophrenia. These conditions often have subtle symptoms. To prevent them, schedule social interactions with colleagues, share difficulties, and relieve stress to maintain mental well-being.
- Radiation exposure
- Daily exposure to computers and phones inevitably causes radiation exposure. Reduce impact by avoiding prolonged sitting, staying hydrated (especially with green tea), using facial mists, or placing small potted plants on your desk to absorb some radiation.
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Most vitamin D comes from sunlight, then from food. Spending 8 hours indoors increases the risk of deficiency.
- Vitamin D deficiency can lead to multiple health issues such as osteoporosis and certain cancers. It may also cause anxiety, depression, and stress.


