Health
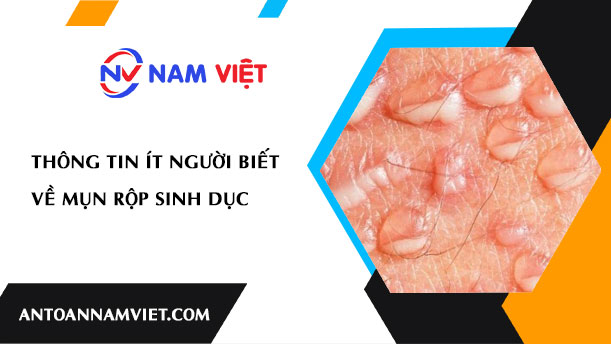
Little-Known Information About Genital Herpes
In the world of health, few people delve into genital herpes, an issue causing much anxiety. This article will take you on a journey to explore strange and important information about this condition. We will discuss the causes, symptoms, and little-known facts about treatment and management. Don’t miss the opportunity to understand this aspect of health better, helping to raise awareness and take comprehensive care of yourself.
I. Introduction to Genital Herpes
In today’s medical world, genital herpes has become an important and complex topic. Caused by the Herpes simplex virus (HSV), genital herpes is not just a reproductive health issue but also relates to many other aspects of overall well-being.
This disease has the potential to recur multiple times throughout life, posing a significant challenge for both patients and the medical community. Although healthy individuals carrying the HSV virus often show no symptoms, a decline in immune resistance, along with factors like inflammation, can activate the virus and cause painful herpes outbreaks.
Furthermore, genital herpes not only affects individual health but also has a major impact on the community. Statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO) indicate that hundreds of millions of people worldwide are infected with HSV-2, creating a challenge for the global health system.
Moreover, genital herpes is closely linked to the risk of HIV infection and can cause dangerous complications, especially for immunocompromised individuals. For pregnant women, the disease can have severe consequences for the fetus, increasing the risk of premature birth and causing death in the womb.

II. Types of Virus Causing Herpes
Genital herpes is not just a simple disease but is also special because it is mainly caused by two types of Herpes simplex virus (HSV): HSV-1 and HSV-2. The diversity in these virus types creates distinct characteristics and affects how herpes develops and spreads.
HSV-1 typically causes oral herpes, commonly appearing on the lips, around the mouth, or on the face. Conversely, HSV-2 is the primary cause of genital herpes, often appearing on or around the genitals, anus, buttocks, and inner thighs of the patient. This distinction is important for understanding the symptoms and transmission methods of each virus type.
Both virus types can be transmitted through close contact with someone who has HSV, not only through conventional sexual intercourse but also through activities like kissing, foreplay, or even non-penetrative sex. This poses a significant challenge in controlling and preventing the spread of herpes, especially since many people carry the virus without any symptoms.

III. Transmission Mode
The transmission mode of genital herpes primarily occurs through sexual activities and close contact. The Herpes simplex virus (HSV) can easily spread from an infected person to another, creating a challenge in controlling and preventing the spread of the disease.
Transmission through sexual contact is common, especially during unprotected sex. HSV can be transmitted through direct contact with infected areas, including the genital region, anus, and inner thighs. This creates a high risk for individuals engaging in unsafe sex, particularly when one partner carries the virus without any symptoms.
Additionally, HSV can also be transmitted through other activities such as kissing, foreplay, or even in cases of non-penetrative sex. This flexibility in transmission mode poses a challenge for reducing infection risk and managing genital herpes within the community.

IV. Frequency of Occurrence and Global Statistics
The frequency of occurrence and global statistics regarding genital herpes are crucial for understanding the scale and impact of this disease on the global community.
According to estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2016, approximately 491.5 million people worldwide were infected with HSV-2, accounting for over 1/10th of the world’s population aged 15 to 49. This figure demonstrates the prevalence of genital herpes and its significant impact on global health.
Simultaneously, WHO also indicated that approximately 3.7 billion people were infected with HSV-1 in the same year, representing about 2/3rds of the world’s population under 50. The enhancement of information and statistics helps us clearly recognize the scale of the problem and the need for effective strategies to control and prevent the transmission of the Herpes virus.
These statistics are not just numbers, but a basis for developing public health strategies aimed at reducing infection risk and providing effective care for those affected by genital herpes globally.

V. Risk of HIV Infection and Dangerous Complications
The risk of HIV infection and dangerous complications related to genital herpes create a complex and challenging health situation.
People infected with HSV-2, the virus causing genital herpes, face a 3-fold higher risk of contracting HIV compared to those not infected with HSV-2. This increases the risk of HIV infection and poses another serious threat to global health.
Among immunocompromised individuals, especially those with advanced HIV infection, herpes can cause severe complications and frequent recurrences. Rare complications include meningitis and disseminated infection, increasing the risk of serious health problems.
These challenges pose a major task in managing and preventing the transmission of genital herpes in the community, while also highlighting the importance of controlling and caring for HIV-infected individuals to prevent potential complications when combined with herpes.

VI. Dangers for Pregnant Women and Newborns
The danger posed to pregnant women and newborns in cases of genital herpes reveals an aspect of the disease that affects not only individual health but also severely impacts the fetus and newborn.
In pregnant women, the Herpes virus tends to hide (remain dormant) in nerve ganglia, making it difficult to cure. When herpes flares up during pregnancy, the virus can increase the risk of premature birth, and the fetus may become infected or even die in the womb. This creates a major challenge in managing the reproductive health of pregnant women infected with the Herpes virus.
For newborns, herpes can occur when the baby comes into contact with HSV while still in the womb. Although the rate is quite low, about 10 per 100,000 births, it carries severe consequences such as neurological disabilities or even death. The risk of neonatal herpes infection is particularly high when the mother contracts HSV for the first time late in pregnancy.
This situation serves as a warning about the necessity of managing and closely monitoring the health of pregnant women with herpes, while also emphasizing the importance of care and health monitoring for newborns at risk of contracting the disease.

VII. Recurrence and Treatment
Recurrence and treatment of genital herpes play a crucial role in managing this condition, optimizing the quality of life for those affected.
Genital herpes often recurs throughout life, especially when immune resistance decreases, such as during periods of anxiety, lack of sleep, or inadequate nutrition. Recurrent episodes usually resolve on their own, and in some individuals, the disease never flares up. However, for those experiencing frequent recurrences (more than 6 episodes per year), treatment with antiviral medication for about 6-12 months is necessary.
Recurrences of HSV-2 are generally milder than the initial outbreak and tend to occur less frequently, causing less concern. Treatment with antiviral drugs has proven effective in controlling and reducing the frequency of genital herpes recurrences.
This not only helps alleviate pain and discomfort but also prevents the transmission of the virus to others. However, effective management of recurrence and treatment requires close cooperation between the patient and doctor, along with maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support immune resistance.

An Toan Nam Viet – a leading unit in providing occupational safety training and workplace environmental monitoring services. We are proud to be a trusted partner for businesses, helping ensure a safe working environment and protecting workers' health.With extensive experience and a team of top experts, we are committed to delivering high-quality services while meeting all regulatory requirements on occupational safety and environmental monitoring.
Our occupational safety training services include educating and raising awareness among employees about safety regulations, equipping them with skills to handle dangerous situations, and implementing accident prevention measures. We continuously update and apply the latest knowledge to ensure your employees always work in a safe environment, minimizing the risk of occupational accidents and protecting their lives.
With our workplace environmental monitoring services, we use the most advanced equipment and methods to measure, monitor, and analyze the quality of air, water, and noise in the working environment. We provide detailed and accurate reports on pollution levels, helping businesses implement solutions to improve working conditions, ensure legal compliance, and create a healthy workplace for employees.
Contact Information:
- Nam Viet Occupational Safety Training and Environmental Monitoring Co., Ltd.
- Phone: 0908 111 791
- Email: lienhe@en.antoannamviet.com
- Website: https://en.antoannamviet.com