Occupational Safety Training for Permanent Magnet Manufacturing
99,000 ₫
Note: The above price is calculated for one person, the price may fluctuate depending on the number of trainees attending the course and market movements. For more accurate pricing support, please refer to the price list or contact our consulting staff directly.
Occupational safety is an important issue in factory manufacturing permanent magnets and needs to be addressed promptly to ensure the health and safety of workers, as well as enhance the reputation of businesses. The Occupational Safety Training course is one of the effective solutions to raise awareness of how to prevent workplace accidents for employees participating in permanent magnet manufacturing.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Overview of Permanent Magnets
a. What is a permanent magnet?
- A permanent magnet is a type of magnet made from a specific magnetic material, capable of creating a strong and stable magnetic field, and retaining its magnetic properties over a long period. It is called “permanent” because it does not lose its magnetic properties over time, unlike temporary magnets which only maintain magnetism temporarily when placed near another magnet or an electromagnet. Permanent magnets are used in many applications, including electronics, mechanical engineering, medical devices, and renewable energy.
- Currently, Vietnam has several companies producing permanent magnets, but most of these products are of limited quality and are mainly processed from imported materials. However, with the development of the electronics, mechanical, and renewable energy industries in Vietnam, there is a demand for high-quality permanent magnets at reasonable prices. Therefore, domestic production of permanent magnets is seen as an opportunity to meet local demand and export to other markets.

b. Machinery for permanent magnet production
The machinery and equipment involved in permanent magnet production include:
- Permanent magnet forming machines: These machines are used to produce permanent magnets from various raw materials such as rare earth elements, iron, cobalt, nickel, and aluminum. The machines can produce magnets with different strengths according to customer requirements.
- Magnet cutting and polishing machines: Machines used to cut and polish permanent magnet components to the required size and shape.
- Magnet testing machines: Machines used to test the quality of magnets after production, ensuring they meet the required quality standards.
- Packing machines: Machines used to pack permanent magnets into packaging or boxes for transport and storage.
- Magnet pressing machines: Machines used to press permanent magnets into various shapes and sizes, suitable for customer needs.
- Vacuum machines: Machines used to create an oxygen-free environment during the production process of permanent magnets, improving product durability and stability.
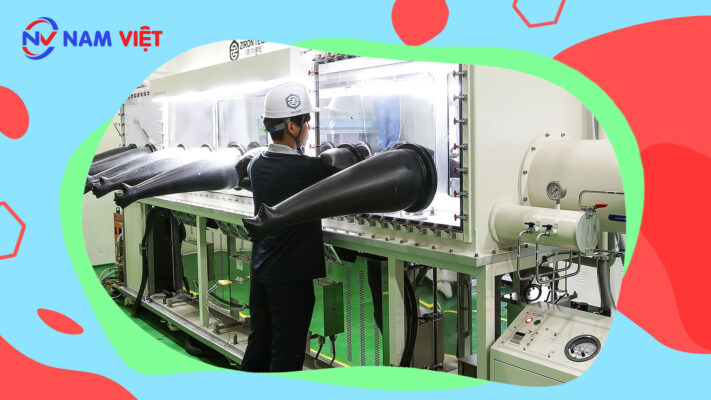

c. Prominent permanent magnet manufacturers
Famous global permanent magnet manufacturers include:
- Hitachi Metals, Ltd.: The largest permanent magnet manufacturer in the world, headquartered in Japan with production facilities in multiple countries.
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.: A leading permanent magnet manufacturer in Japan, capable of producing high-strength permanent magnets for various industries.
- Arnold Magnetic Technologies Corporation: The largest permanent magnet manufacturer in the United States, supplying magnets for industries including medical, motors, and electronics.
- Adams Magnetic Products Co.: A US-based leading permanent magnet manufacturer providing magnets for industries such as automotive, medical, and industrial machinery.
- TDK Corporation: Headquartered in Japan, producing high-quality permanent magnets for electronics, automotive, and renewable energy industries.
d. Specific roles in a permanent magnet manufacturing plant
Group 1
- Chief Executive Officer, Deputy CEO, department heads in the permanent magnet manufacturing plant.
Group 2
- Safety officers: manage safety in the plant, design safety procedures, monitor and enforce employee compliance with safe working processes.
Group 3
- Production: After a design is finalized, factory workers produce permanent magnets through processes such as casting, cutting, grinding, plating, and quality inspection.
- Quality control: Permanent magnets are tested using measuring devices such as Gauss meters, mass measurement machines, hardness testers, etc., to ensure they meet quality standards.
- Packing and shipping: After production and quality inspection, permanent magnets are packed and shipped to customers.
- Maintenance and repair: The plant may have maintenance and repair departments to ensure continuous operation of production equipment and minimize failures.
Group 4
- Office, service, sales, and marketing roles.
- Production management, quality management, human resource management, material management, and financial accounting management.
- Design: The design department develops new permanent magnet models based on customer requirements or for research and product development.
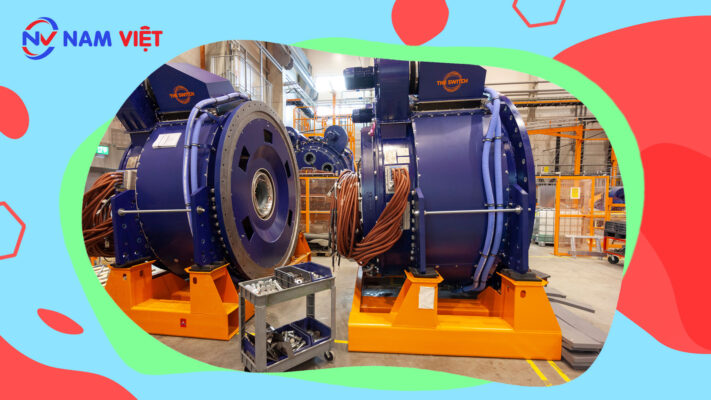

2. Overview of occupational safety training for permanent magnet production
In this article, we focus on issues related to Group 3, because Group 3 directly participates in the production process and is exposed to the highest occupational safety risks. For more information on other groups, see here.
a. What is Group 3 occupational safety training?
- Group 3 occupational safety training consists of sessions that provide workers with awareness and knowledge on preventing workplace accidents.
- The training course helps workers recognize and avoid hazards, reducing the risk of workplace accidents during their tasks.
REGISTER FOR OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY TRAINING SERVICE
b. Training duration
Initial occupational safety training
- Total training time is at least 24 hours, including examination time.
- 8 hours of theory on the policy and legal framework regarding occupational safety and hygiene
- 8 hours of theory on basic knowledge of occupational safety and hygiene
- 4 hours of theory on specialized training content
- 2 hours of practical training on specialized content
- 2 hours of theoretical examination at the end of the course
The safety training center will schedule multiple sessions depending on worker availability. Typically, there are 6 training sessions over 3 days, provided the manufacturing company can arrange continuous training time.
Periodic occupational safety training
- Before the occupational safety card expires, workers wishing to renew it must complete a periodic occupational safety training, with the training duration being at least 50% of the initial training duration.
Explanation: The total duration of periodic occupational safety training is at least 12 hours, including examination time. Upon completion and passing the exam, the worker’s occupational safety card will be renewed.
c. Training content
| No. | TRAINING CONTENT | TRAINING HOURS | |||
| Total | Including | ||||
| Theory | Practical | Examination | |||
| I | Policy and legal system regarding occupational safety and hygiene | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | Overview of the regulatory framework on occupational safety and hygiene. | 6 | 6 | ||
| 2 | System of standards and technical regulations for occupational safety and hygiene. | 1 | 1 | ||
| 3 | Specific regulations by government authorities regarding occupational safety and hygiene when constructing, expanding, or renovating facilities, and producing, using, storing, or inspecting machines, equipment, materials, or substances with strict safety and hygiene requirements. | 1 | 1 | ||
| II | Basic knowledge of occupational safety and hygiene | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | Basic knowledge of hazards and harmful factors in the workplace. | 4 | 4 | ||
| 2 | Methods to improve working conditions. | 1 | 1 | ||
| 3 | Safety culture in production and business. | 1 | 1 | ||
| 4 | Rights and responsibilities of employers and employees; policies on occupational safety and hygiene for employees; functions and duties of the safety network. | 1 | 1 | ||
| 5 | Rules on safety and hygiene, safety signs, use of protective equipment, first aid skills, and occupational disease prevention. | 1 | 1 | ||
| III | Specialized training content | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
| Comprehensive knowledge of machines, equipment, substances causing hazards; risk analysis, management, safe working procedures for machines, equipment, and hazardous substances. | 6 | 4 | 2 | ||
| IV | End-of-course safety examination | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 24 | 22 | 2 | ||
See more training content for all 6 groups
d. Occupational safety card
After completing the occupational safety training course and passing the exam, workers will be issued a safety card (commonly called a Group 3 occupational safety certificate).
The Group 3 safety card shows details such as full name, date of birth, job, and specific working environment, as well as training duration, red stamp, and signature confirming completion.
According to the card issuance regulations in Clause 2 of Article 24, Decree 44/2016/ND-CP, there are two cases:
- If the employer and employee have a labor contract, the employer must sign and stamp the safety card for the Group 3 employee after completing the training and passing the exam.
- If the worker is freelance or temporary and does not have a labor contract, the training unit must sign and stamp the safety card after the worker completes the training and passes the exam.

3. Identifying Hazards Affecting Workers in Permanent Magnet Manufacturing
During the process of manufacturing permanent magnets, workers may encounter various hazards, including:
- Permanent magnet manufacturing equipment operates using electricity. Therefore, there is a risk of electric shock if safety procedures and measures are not properly followed.
- During permanent magnet production, workers may be exposed to X-rays and gamma rays from radioactive sources such as Cobalt-60, Iodine-131, Strontium-90, etc. Without wearing full protective equipment and following proper procedures, workers’ health may be affected.
- Machines in the permanent magnet factory operate continuously at high noise levels. If workers do not wear hearing protection, they may suffer hearing damage.
- Some permanent magnet manufacturing processes use hazardous chemicals such as nitric acid, sulfuric acid, lead, nickel, cobalt, etc. Without proper protective equipment and safety procedures, workers may be harmed.
- During permanent magnet manufacturing, molten materials are used to form magnets. Workers must wear full protective equipment to avoid burns.
- There is a risk of explosion when using gas or if materials collide during permanent magnet production.
4. Common Workplace Accidents for Workers in Permanent Magnet Manufacturing
During permanent magnet production, workers may face many potential hazards. Common workplace accidents in permanent magnet manufacturing include:
- Injury from heavy objects: Moving and lifting heavy equipment, using tools and machinery may lead to accidents, including collisions with heavy objects or being struck by falling objects.
- Muscle injuries: Manufacturing permanent magnets requires extensive use of body parts, especially hands, neck, and back. Improper use of these body parts can cause pain, swelling, or muscle injuries.
- Electrical hazards: Permanent magnet production requires the use of electrical devices and machinery, so workers may be at risk of electric shock or burns.
- Chemical hazards: Workers may be exposed to hazardous chemicals that can irritate the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
- Dust exposure: Some stages of permanent magnet production generate metal dust and dust from liquids. Without proper protective equipment, workers may inhale dust, leading to health issues.
5. Safety Measures in Permanent Magnet Manufacturing
To ensure the safety of workers in permanent magnet production, the following measures should be applied:
- Use protective equipment: Workers should wear protective gear such as helmets, safety shoes, gloves, goggles, masks, etc., to safeguard body parts and protect against hazardous substances and accidents.
- Safety training and guidance: Employees should be trained on production procedures, safe equipment usage, accident handling, and rescue methods.
- Maintenance and repair: Regularly inspect equipment, machinery, and tools to ensure proper operation and avoid hazards. Faulty or damaged items should be repaired or replaced immediately.
- Chemical management and storage: Chemicals should be properly managed and stored to prevent incidents harmful to workers. Material Safety Data Sheets should be used to guide usage, storage, and transportation.
- Energy source control: Ensure energy sources are managed properly to prevent fire, explosion, or other workplace accidents.
- Safety supervision during production: Management should monitor and inspect work to ensure production procedures are followed and safety measures are implemented.
- Accident investigation: When an accident occurs, investigate the cause to implement preventive measures and reduce recurrence risk.
- Regular workplace environment monitoring in factories to collect and analyze harmful factors, then adjust to reduce hazards and prevent occupational diseases.
6. Benefits of Occupational Safety Training in Permanent Magnet Manufacturing
An Toan Nam Viet provides the following benefits for businesses after completing occupational safety training courses in accordance with Decree 44/2016/ND-CP on occupational safety and hygiene for companies:
- Workers can recognize potential workplace hazards and take preventive measures to avoid accidents.
- Businesses can establish risk prevention measures in production, operation, and maintenance processes.
- Reduce costs associated with potential safety incidents.
- Uninterrupted production increases labor productivity and product quality.
- Compliance with labor safety laws reduces legal risks.
- Enhances reputation and professionalism, thereby elevating the company’s brand.
Nam Viet training courses help individuals prevent external hazards and avoid injuries or even fatal accidents.
REGISTER FOR OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY TRAINING SERVICE
7. Customer Feedback After Completing Permanent Magnet Safety Training
An Toan Nam Viet has many years of experience accompanying enterprises in Vietnam, especially in southern provinces. This responsibility is highly valued, so our Occupational Safety Training is increasingly professional. Our growth is motivated by positive feedback and suggestions from businesses. Below are feedbacks from our partners.
Hoa Dat Construction and Trading Joint Stock Company
“Nam Viet’s service helped us simplify occupational safety and complete safety documentation for work processes. The advisory team responded promptly and enthusiastically to our questions. 5 stars for Nam Viet.”
See more customer interviews after using the service of An Toan Nam Viet
8. Occupational Safety Training Capability of An Toan Nam Viet
An Toan Nam Viet is a reputable and high-quality occupational safety training center in Vietnam. Training sessions are conducted continuously at factories, production plants, or construction sites nationwide (all 63 provinces).
REGISTER FOR OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY TRAINING SERVICE
Occupational Safety Training License
- An Toan Nam Viet has been certified by the Department of Safety under the Ministry of Labor, War Invalids, and Social Affairs, ensuring compliance with occupational safety and hygiene training standards, reinforcing our training capabilities.

Training Materials and Lectures
- Before being included in OHS training courses, materials are reviewed to ensure knowledge accuracy and effectiveness.
- Instructors’ teaching methods follow An Toan Nam Viet standards, developed by experts in occupational safety and hygiene training to maximize learning efficiency for trainees.
Facilities
- Controlling classroom factors improves teaching efficiency and knowledge absorption.
- Training facilities are spacious, meeting standards for area, lighting, and training equipment.
9. Nationwide Reputable Occupational Safety Training Center
At An Toan Nam Viet, we prioritize professional occupational safety training. Our mission is to equip workers with knowledge to protect themselves, contributing to national development.
To ensure effective training, we meticulously prepare tools, teaching materials, audio, and lighting.
Our instructors are experts with years of experience, including research on hazard identification across all industries and prevention measures.
Lectures are practical, engaging, and easy for workers to understand, adhering to Decree 44/2016/ND-CP.
Our training center is proud to offer professional occupational safety training with advantages:
- Competitive training costs while maintaining quality.
- Flexible training schedules aligned with company production.
- Fast certification procedures compliant with law.
- Experienced instructors.
- Controlled classrooms for effective teaching and knowledge absorption.
- Lectures tailored to occupational safety in enterprises.
- Dedicated, professional support for customers.

10. Additional References for Permanent Magnet Occupational Safety Training
- Permanent Magnet Safety Training Materials
- Occupational Safety Training Material Set
- Occupational Safety Training Test Set
- Permanent Magnet Occupational Safety Quiz
- Permanent Magnet Occupational Safety Training Slides
1 review for Occupational Safety Training for Permanent Magnet Manufacturing
No comments yet















namchinh.haiphong341
Dịch vụ ở đây tốt nhé!